Oral cancer is a serious health issue, yet many people...
Read More- Home
- Blogs
- Oral Cancer
The Link Between Tobacco and Oral Cancer: Understanding the Risks
Book Your Consultation
Our team is here to give you specialized care and encouragement that will suit your needs
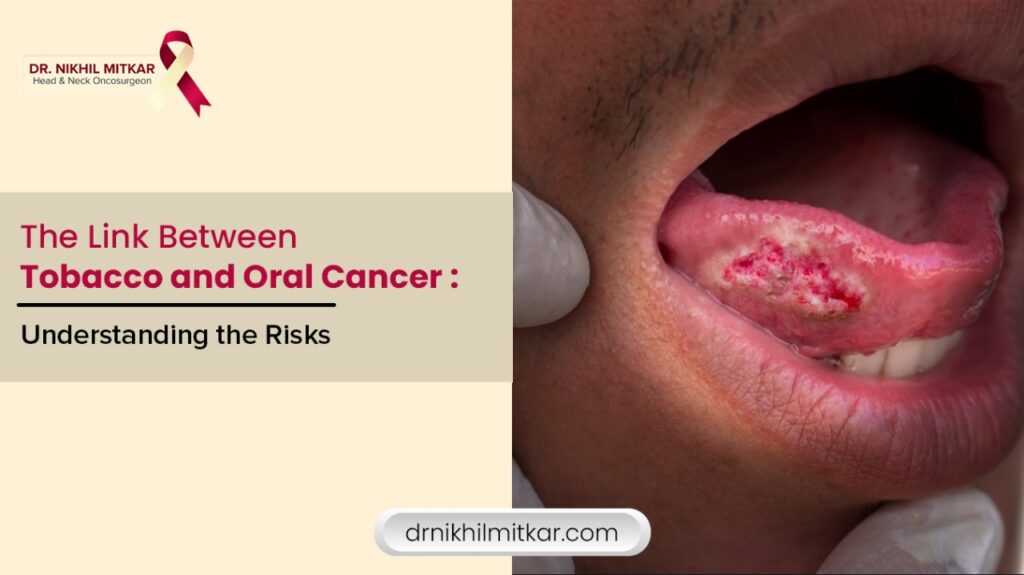
Tobacco use is one of the most significant and preventable causes of cancer worldwide. While many associate tobacco with lung cancer, its devastating effects are far-reaching, contributing to the development of several other cancers, including oral cancer. Oral cancer refers to malignancies that occur in the mouth, including the lips, cheeks, tongue, gums, the roof of the mouth, the floor of the mouth, and the throat (oropharynx). Both smoking and smokeless forms of tobacco are responsible for a substantial percentage of oral cancer cases globally.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the connection between tobacco and oral cancer, the mechanisms through which tobacco causes harm, and why quitting tobacco is essential for reducing the risk of this life-threatening condition.
Tobacco’s Harmful Components
Tobacco products, whether smoked or chewed, contain a wide range of harmful chemicals. Among the 7,000+ chemicals in tobacco smoke, at least 70 are known carcinogens—substances that directly cause cancer. These chemicals include:
- Nicotine: Although primarily responsible for addiction, nicotine itself isn't a direct carcinogen, but it plays an essential role in promoting cancer by fostering environments conducive to abnormal cell growth.
- Formaldehyde: Commonly used in embalming, this toxic substance can damage DNA and lead to mutations that trigger cancer.
- Benzene:This chemical, also found in gasoline, can cause significant genetic damage and is linked to various cancers.
- Tar: A sticky substance that coats the lungs and mouth, tar is full of carcinogens that can penetrate the cells lining the mouth and throat.
- Nitrosamines: Found in both smoked and smokeless tobacco, these are among the most potent cancer-causing chemicals. They are formed during the processing and curing of tobacco.
Chewing tobacco also contains high levels of nitrosamines, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and other harmful chemicals. Contrary to popular belief, smokeless tobacco can sometimes be even more carcinogenic than smoking tobacco, particularly when it’s kept in direct contact with the oral tissues for extended periods.
How Tobacco Causes Oral Cancer
When tobacco products are consumed, the harmful chemicals they contain come into direct contact with the delicate tissues of the mouth. Over time, this continuous exposure leads to cellular damage, which can eventually cause mutations in the DNA of cells. Mutations disrupt normal cell growth and function, leading to uncontrolled proliferation, which can result in tumor formation.
The Mechanism of Damage:
1. Direct Contact with Toxins: In smokers, the inhalation of tobacco smoke exposes the entire oral cavity, throat, and lungs to toxic chemicals. The cells lining the mouth are particularly vulnerable to the effects of these carcinogens. In smokeless tobacco users, the direct placement of tobacco in the mouth allows these toxins to penetrate the mucous membranes, damaging the cells even further.
2. Cellular Mutations: Repeated exposure to carcinogens in tobacco causes mutations in the DNA of oral cells. These mutations interfere with normal cellular processes, such as apoptosis (programmed cell death), which is a natural mechanism to eliminate damaged or abnormal cells. When this process is disrupted, abnormal cells can begin to accumulate and divide uncontrollably, forming cancerous tumors.
3. Weakened Immune Response: Tobacco use weakens the body’s immune response, making it harder to detect and repair damaged cells. A compromised immune system is less effective in fighting off early-stage cancer cells, allowing them to grow and spread.
4. Inflammation and Tissue Damage: Tobacco use also causes chronic inflammation of the oral tissues, leading to the formation of precancerous lesions such as leukoplakia (white patches) and erythroplakia (red patches). These lesions are not cancerous in themselves, but they can develop into oral cancer if left untreated.
Types of Tobacco-Related Oral Cancers
Oral cancers linked to tobacco use can occur in various parts of the mouth, including:
- Lips: Smoking, as well as prolonged sun exposure, can cause cancer of the lips. Smokers often hold cigarettes between their lips, exposing them to high concentrations of carcinogens.
- Tongue: Tobacco smoke and chew are strongly associated with tongue cancer, especially on the sides and undersurface of the tongue.
- Gums and Cheeks: Chewing tobacco users are at particular risk for cancers of the gums, cheeks, and inner surfaces of the lips. The continuous presence of tobacco in these areas subjects them to constant exposure to harmful chemicals.
- Throat (Oropharynx): Smoking is a primary cause of cancers that occur in the back of the throat and tonsils. Tobacco carcinogens can reach deep into the throat tissues, where they cause damage over time.
Risk Factors for Oral Cancer from Tobacco Use
Several factors increase the risk of developing oral cancer from tobacco use:
- Duration of Tobacco Use: The longer a person uses tobacco, the higher their risk. Oral cancer can develop after years or even decades of tobacco use.
- Type of Tobacco Product: Both smoking and smokeless tobacco products are dangerous, but smokeless tobacco users often develop cancer in the parts of the mouth where the tobacco is placed.
- Alcohol Use: Alcohol and tobacco together create a particularly deadly combination. Alcohol can act as a solvent, allowing carcinogens to penetrate the tissues more easily, increasing the risk of cancer by up to 30 times when both are used together.
- HPV Infection:The human papillomavirus (HPV) is a significant risk factor for throat cancers, particularly when combined with tobacco use.
Preventing Tobacco-Related Oral Cancer
The most effective way to prevent oral cancer caused by tobacco is to quit using tobacco products. Stopping smoking and chewing tobacco not only reduces the risk of cancer but also improves overall oral and general health. Here are some key prevention strategies:
- Quitting Tobacco: Tobacco cessation can drastically reduce the risk of oral cancer, even for long-term users. Research shows that after quitting, the risk gradually decreases over time. Within 10 to 15 years of quitting, the risk of oral cancer may return to that of a non-smoker.
- Regular Screening: Regular dental checkups and oral cancer screenings are critical, especially for current and former tobacco users. Dentists can detect early signs of oral cancer, such as unusual growths, sores, or patches, that might go unnoticed otherwise.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables, exercising regularly, and avoiding excessive alcohol use can all reduce the risk of oral cancer.
Conclusion
Tobacco use is one of the leading causes of oral cancer, with devastating consequences for individuals’ health. The carcinogens found in tobacco products—whether smoked or chewed—cause significant damage to the cells in the mouth and throat, leading to mutations that can eventually develop into cancer. Quitting tobacco, regular screening, and adopting a healthy lifestyle are the most effective ways to prevent this deadly disease. Raising awareness about the risks of tobacco use and its link to oral cancer is crucial in the fight to reduce cancer rates and promote healthier lives.
Oral Cancer Aftercare: Your Guide to Recovery
Recovering from oral cancer treatment is a journey that requires...
Read MoreThe Link Between Tobacco and Oral Cancer: Understanding the Risks
Tobacco use is one of the most significant and preventable...
Read MoreEarly Detection of Oral Cancer: Why It Matters and How You Can Protect Yourself
Home Blogs Oral Cancer Early Detection of Oral Cancer: Why...
Read MoreBook Your Consultation
Begin the healing process now. Our team is here to give you specialized care and encouragement that will suit your needs
What Our Patients Say
My husband, was initially misdiagnosed, and his first operation failed. A neighbor recommended Dr. Nikhil Mitkar. Dr. Nikhil thoroughly explained the situation, conducted all necessary tests, and performed a successful operation at Fauziya Hospital. Despite our anxiety, Dr. Nikhil’s support and systematic approach brought us peace. Now, he is complication-free, and we’re grateful for Dr. Nikhil's care.
Seema Shashikant
Life-Saving Expertise
and Care
Meeting Dr. Nikhil Mitkar was life-changing. I was misdiagnosed with an ulcer, but Dr. Nikhil identified my cancer and treated me successfully. His dedication and expertise saved me. The operation was done with care, and I recovered quickly. The treatment was affordable, and now I’m healthy again. I highly recommend Dr. Nikhil to anyone battling cancer. His approach and commitment to patients make all the difference.
Mohammed sami
From Misdiagnosis to Full Recovery
My husband discovered cancer in 2020 after initially thinking it was just an infection. We tried various treatments, including expensive Ayurvedic medicines and chemo. A friend recommended Dr. Nikhil Mitkar, who guided us through the final step. He performed the operation at a lower cost, and my husband has improved by 50%. Dr. Nikhil’s guidance and care were invaluable. I highly recommend him for the best treatment possible.
Pratiksha
Compassionate Cancer Treatment Journey
For more information about our services or to schedule an appointment, please contact Dr. Nikhil & Our team is here to provide the best Cancer care in Mumbai.
Top Services
Quick Links
Need Support
Please explore our contact page to find relevant information and assistance.
- nikhilmitkar37@gmail.com
- +91 99304 73676
- dr_nikhil_mitkar_
- Head & Neck Cancer Clinic, 6, opposite New English School Marg, Government Colony, Bandra East, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400051
© 2025 Dr. Nikhil Mitkar. All rights reserved.
